50 Product Designs Concept Manufacture Pdf Writer
ABOUT AUTHORS:S.P.Sethy., Tahseen Sameena, Prathima Patil, K.ShailajaDepartment Of Pharmaceutical Chemistry.Sushrut Institute of PharmacyTaddanpally (V), Pulkal (M), Medak-502293ABSTRACT:The complexity of today’s pharmaceutical market requires more efficient drug development and production. Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) has the opportunity to make pharmaceutical production more effective and with lower risk – even in this vastly complex environment. The product lifecycle management creates and manages a company's product-related intellectual capital starting from an idea to its final retreat. In pharmaceutical industry, it benefits through enhancing the lifespan of patent and pricing strategies. Improved patient compliance, revenue growth, expanded clinical benefits; cost advantages life extension exclusivity and quicker market launch are amongst the main applications of product lifecycle management. Leaders are actively implementing PLM and are reaping the benefits of fewer problems, lower costs, higher yields, employees armed to make good decisions, and audits that make everyone more confident as they access the information they need. The present manuscript focuses on product lifecycle management, problems and the key solutions for a successful product lifecycle management in pharmaceuticals.
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-2051INTRODUCTION:Product lifecycle management(PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its conception, through design and manufacture, to service and disposal. PLM forms the product information backbone for a company and its extended enterprise. PHASES OF PRODUCT LIFECYCLE AND RELATED TECHNOLOGIES:PHASE 1: CONCEIVE IMAGINE, SPECIFY, PLAN, INNOVATEThe first stage is the definition of the product requirements based on customer, company, market and regulatory bodies’ viewpoints.
From this specification, the product's major technical parameters can be defined. In parallel, the initial concept design work is performed defining the aesthetics of the product together with its main functional aspects.
Many different media are used for these processes, from pencil and paper to clay models to 3D CAID (computer-aided industrial design software). In some concepts, the investment of resources into research or analysis-of-options may be included in the conception phase – e.g. Bringing the technology to a level of maturity sufficient to move to the next phase. However, life-cycle engineering is iterative. It is always possible that something doesn't work well in any phase enough to back up into a prior phase – perhaps all the way back to conception or research.
There are many examples to draw from.PHASE 2: DESIGN DESCRIBE, DEFINE, DEVELOP, TEST, ANALYZE AND VALIDATEThis is where the detailed design and development of the products form starts, progressing to prototype testing, through pilot release to full product launch. It can also involve redesign and ramp for improvement to existing products as well as planned obsolescence. The main tool used for design and development is CAD. This can be simple 2D drawing / drafting or 3D parametric feature based solid/surface modeling. Such software includes technology such as Hybrid Modeling, Reverse Engineering, KBE (knowledge-based engineering), NDT (Nondestructive testing), and Assembly construction. This step covers many engineering disciplines including: mechanical, electrical, electronic, software (embedded), and domain-specific, such as architectural, aerospace, automotive. Along with the actual creation of geometry there is the analysis of the components and product assemblies.
Simulation, validation and optimization tasks are carried out using CAE (computer-aided engineering) software either integrated in the CAD package or stand-alone. These are used to perform tasks such as:- Stress analysis, FEA (finite element analysis); kinematics; computational fluid dynamics(CFD); and mechanical event simulation (MES). CAQ (computer-aided quality) is used for tasks such as Dimensional tolerance (engineering) analysis. Another task performed at this stage is the sourcing of bought out components, possibly with the aid of procurement systems.PHASE 3: REALIZE MANUFACTURE, MAKE, BUILD, PROCURE, PRODUCE, SELL AND DELIVEROnce the design of the product’s components is complete the method of manufacturing is defined. This includes CAD tasks such as tool design; creation of CNC Machining instructions for the product’s parts as well as tools to manufacture those parts, using integrated or separate CAM computer-aided manufacturing software. This will also involve analysis tools for process simulation for operations such as casting, molding, and die press forming.
Once the manufacturing method has been identified CPM comes into play. This involves CAPE (computer-aided production engineering) or CAP/CAPP – (production planning) tools for carrying out factory, plant and facility layout and production simulation. For example: press-line simulation; and industrial ergonomics; as well as tool selection management. Once components are manufactured their geometrical form and size can be checked against the original CAD data with the use of computer-aided inspection equipment and software. Parallel to the engineering tasks, sales product configuration and marketing documentation work take place.
This could include transferring engineering data (geometry and part list data) to a web based sales configuration and other desktop publishing systems.PHASE 4: SERVICE USE, OPERATE, MAINTAIN, SUPPORT, SUSTAIN, PHASE-OUT, RETIRE, RECYCLE AND DISPOSALThe final phase of the lifecycle involves managing of in service information. Providing customers and service engineers with support information for repair and maintenance, as well as waste management/recycling information. This involves using tools such as Maintenance, Repair and Operations Management (MRO) software. There is an end-of-life to every product. Whether it be disposal or destruction of material objects or information, this needs to be considered since it may not be free from ramifications.PRODUCT AND PROCESS LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT (PPLM):Product and process lifecycle management (PPLM) is an alternate genre of PLM in which the process by which the product is made is just as important as the product itself. Typically, this is the life sciences and advanced specialty chemicals markets.
The process behind the manufacture of a given compound is a key element of the regulatory filing for a new drug application. As such, PPLM seeks to manage information around the development of the process in a similar fashion that baseline PLM talks about managing information around development of the product. One variant of PPLM implementations are Process Development Execution Systems(PDES). They typically implement the whole development cycle of high-tech manufacturing technology developments, from initial conception, through development and into manufacture. PDES integrate people with different backgrounds from potentially different legal entities, data, information and knowledge and business processes.NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT ATFIND OUT AT OUR DATABASE.
New Product Development Process Sample EssayThe world is full of opportunities to satisfy unmet needs by creating new products and services. However, the challenge is determining the product of service that will help the organization to meet its objectives.
This is because the product that a business chooses must be able to meet the overall objectives of the business, earn the company the desired profit, meet the company’s strategic positioning goals, and conform to the operational requirements of the business. This means that every good product idea is no always visible. It is therefore important that a company does thorough research of the of the new product idea before it begins to mass-produce the product so to avoid new product failure. This paper will outline the process of creating a new productThere are four main stages in the new product development process: idea generation, idea screening, idea evaluation, development of the product, and product commercialization. According to Annacchino (2003), the market is full of opportunities, ideas, concepts, and triggers of new product. Opportunities refer to identifiable business of technology gaps that a business can exploit in order to gain a competitive advantage or solve customer’s problems. An idea refers to a perception of a new product or idea that helps a business to solve the needs that exist in the market (Ahmed, 2014).A concept refers to a description of a technology needs and the customer benefits that will result from a conceived idea.
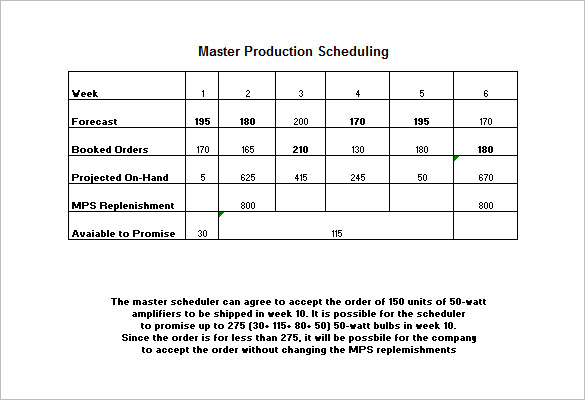
Triggers, on the other hand, refer to factors within the market that promote the creation of new products ( Urban, Hauser, & Urban, 1993). Spectracam milling keygen. One of the triggers to new product idea is advancement in technology, which creates a new opportunity to improve existing products.
Another trigger is increase in competition, which forces business organizations to improve their products in order to remain relevant in the market. A company should choose only the ideas that fit into its overall objectives and strategies ( Veryzer, 1998).The second step in new product development is screening existing business ideas. The process of screening will help the business to sort out those ideas that fit with the business’ market and technological area of focus. The managers should also look at whether the idea has a potential for growth, is technologically viable, and is legal (Annacchino, 2003).The third process in new product development is conceptualizing the product idea.

One of the main activities that take place in this process is market research. Carrying out the market research helps the managers determine whether there is enough demand for then new product.
The data that the business collects during the market research stage helps it in designing a projection of the costs, revenues, and profit from the new product. This will help the managers to determine whether the new product is financially viable. The business should also design a number of working prototypes for the new product. In a restaurant business, the new product prototype can be a new dish or a combination of dishes (Urban, Hauser, & Urban, 1993).The fourth process of the new product development process is the development of product. During this process, the managers must design the final product and manufacturing the new product or service. This process also involves determining the selling price for the new price, estimating the sales volume, and conducting a market test. This process gives the business a chance to test the new product in the market to determine whether there is any real demand for it before full commercialization (Calantone & Benedetto, 1988).
50 Product Designs Concept Manufacture Pdf Writers
The test marketing helps the business to test the performance of the new product without inventing too many resources in a full-blown marketing campaign.The fifth step in new product development is the commercialization or the launch of the new product. During this stage, the business should increase the product production and delivery so that the product is available to a larger share of the market. This will also involve observing the marketing data and production costs to determine whether the product will start earning profits as the company increases its sales volume.
The company should also design a marketing promotion strategy to market the new product and create awareness in the market (Ahmed, 2014).The process of developing a new services such as those offered in restaurants is different to that the process of developing. The differences result from the differences between products and services, namely, intangibility, heterogeneity, perishability, inseparability, and simultaneity in production and consumption of the product and service. These unique features of services make the process of designing and marketing the new service different from that of designing and marketing tangible products. For example, intangibility of services makes it difficult to share the new service idea with others in the organization.
This therefore means that the service development team must make the service tangible by the use of flow charts and pictures. Secondly, the new product ties the clients to the service provider or employees of the firm. This means that designing a new service involves more work in training the personnel within the firm in order to offer the new service to the clients (Annacchino, 2003).In conclusion, the process of designing a new product or service begins by identifying the opportunities available in the market. Next, the managers must screen the ideas, evaluation the available pool of ideas, develop the product, and commercialize the product. Once the company has commercialized the product, it must design a marketing strategy to promote the new product or service in order to increase awareness among the customers.
However, when designing and marketing a product, a firm must keep in mind the unique features of a service and adjust the product development and promotion strategy to match these features.ReferencesAhmed, R. New product development: strategy & implementation mechanism based on primary & secondary data research in pharmaceutical industry. International Journal of Management, IT and Engineering, 4(5), 152-176.Calantone, R. J., & Benedetto, C. An integrative model of the new product development process.
Journal of Product Innovation Management, 5(3), 201-215.Schilling, M. A., & Hill, C. Managing the new product development process: strategic imperatives. The Academy of Management Executive, 12(3), 67-81.Urban, G.
L., Hauser, J. R., & Urban, G. Design and marketing of new products. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.Veryzer, R. Discontinuous innovation and the new product development process. Journal of product innovation management, 15(4), 304-321.